& Construction

Integrated BIM tools, including Revit, AutoCAD, and Civil 3D
& Manufacturing

Professional CAD/CAM tools built on Inventor and AutoCAD
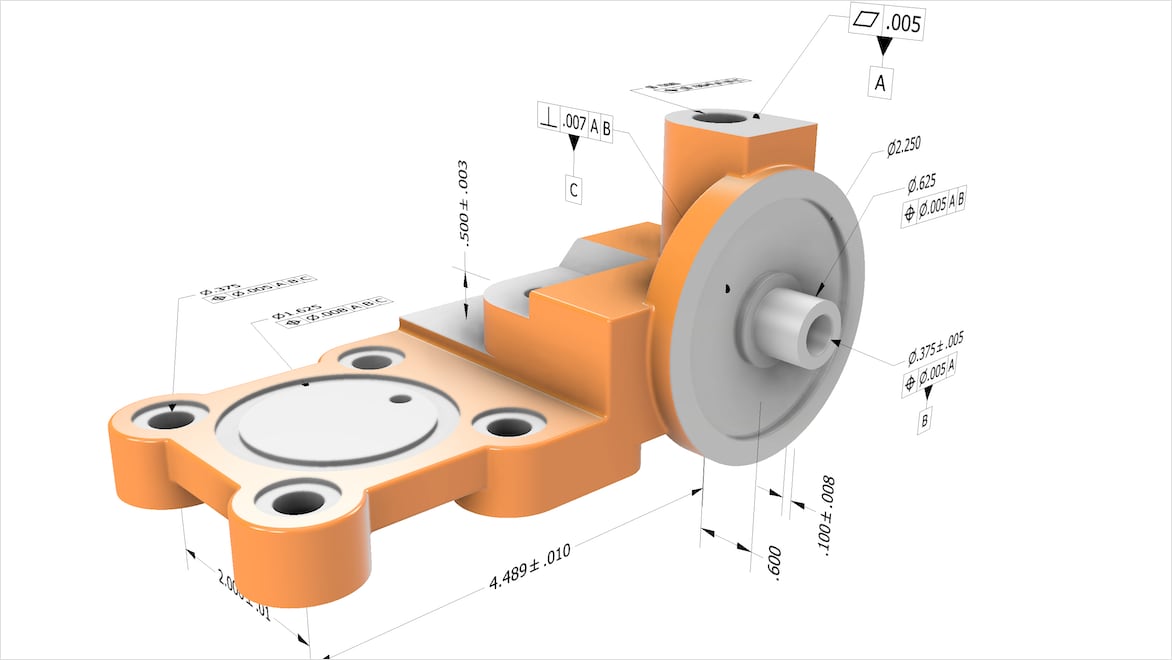
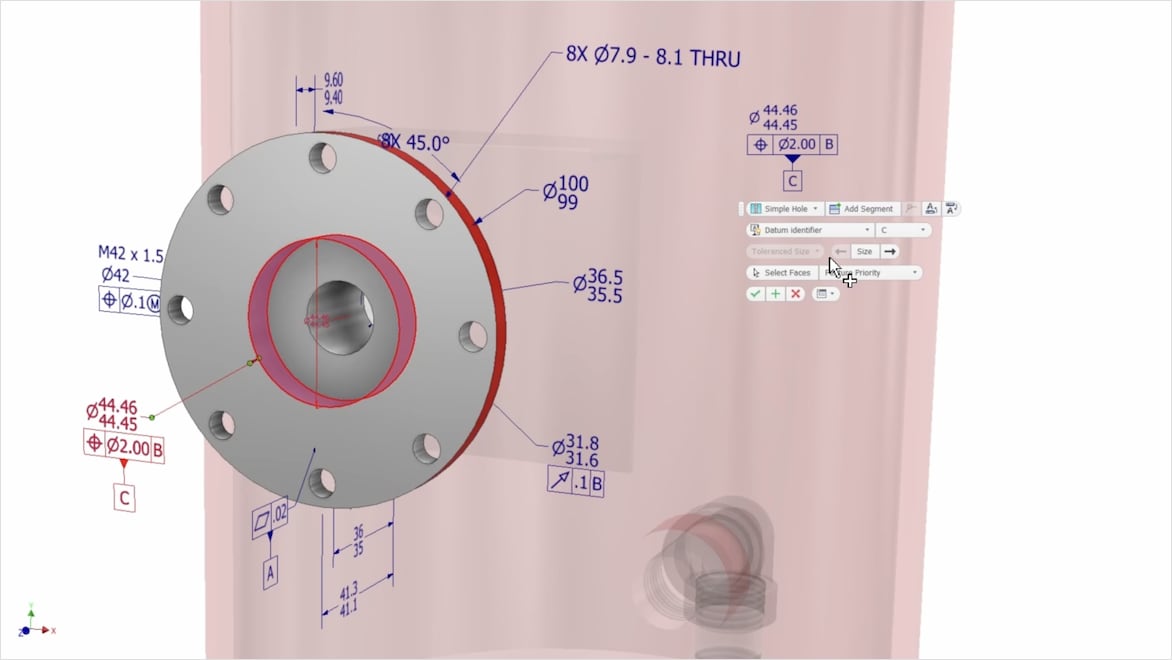
Model-based definition (MBD) makes 3D models your central source for all product manufacturing information (PMI) throughout the lifecycle.
Instead of using 2D engineering drawings, MBD embeds all product data—such as dimensions, tolerances, and material specifications—directly into the 3D model. Get a single, reliable reference that streamlines your design, manufacturing, and quality control process.
2D drawings have long been the cornerstone of product development, capturing design intent and manufacturing details. But as products and assemblies became more complex, this traditional method began to fall short.
Producing and interpreting 2D drawings requires significant time, skill, and experience. They can be prone to misinterpretation, leading to costly production, delays, rework, and material waste.
Enter MBD. Driven by the need for tighter tolerances and higher precision—especially in demanding industries like aerospace—MBD was codified in the 2003 ASME Y14.41 Standard “Digital Product Definition Data Practices.”
This standard, backed by industry leaders such as Boeing and General Motors, introduced a new way to capture and communicate product data: placing all necessary information within the 3D CAD model.
MBD eliminates the need for separate 2D drawings by integrating geometric dimensioning and tolerancing (GD&T), materials, configurations, and more into one accessible 3D model. Manufacturing your products becomes more accurate, and you can provide stakeholders with a clear, unambiguous source of truth.
Modern MBD software builds on this foundation, making it easier than ever to implement standardized, universally understood annotations within 3D models.
Product data management (PDM) systems take this a step further by securely managing your model’s revision. This ensures that everyone involved—from designers to manufacturers—has access to the right information at the right time.
By automating manual processes and relying less on 2D drawings, MBD massively shortens your development cycles. According to one NIST study, MBD can cut the design-manufacturing-inspection process by up to 75%.
As a result, MBD is now fueling the rise of model-based enterprises (MBEs). Companies use the more efficient approach to optimize operations across internal teams, suppliers, and partners.
Powerful product design and engineering tools for 3D mechanical design, simulation, visualization, and documentation.
Inventor Tolerance Analysis software is designed to understand the cost impact of dimensional variation.
Get Inventor + AutoCAD + Autodesk Fusion + more—Professional-grade tools for product development and manufacturing planning.
Discover how MBD software transforms your workflow, making it more efficient, accurate, and collaborative across every stage of product development.
MBD software gets rid of the need for manual data re-entry by standardizing annotation across programs, speeding up design, manufacturing, and inspection processes. You can focus more on innovation and spend less time on tedious documentation tasks.
With MBD, your 3D models carry precise quality requirements embedded directly into the design. This reduces communication errors, shortens manufacturing prep time, and ensures your products meet exact specifications with fewer mistakes.
MBD keeps your data with the model through every stage of development. This seamless integration means that teams across departments can easily see the latest information, improving collaboration and keeping everyone on the same page.
By ditching paper-based documentation, MBD significantly reduces waste from scraps and rework caused by misreading 2D drawings. Everything is digital, leading to a more sustainable and efficient workflow.
Managing product data digitally with MBD software cuts costs—you don’t need the labor or material expenses of producing, storing, and managing 2D drawings. Your process is more organized, and your project costs less.
MBD software makes it easier to meet industry standards and compliance requirements by keeping all necessary documentation within the digital model. This allows you to stay compliant with less effort and helps simplify audits.
MBD supports more sustainable design and manufacturing by reducing material waste, energy use, and reliance on physical resources.
By embedding all product data directly into the 3D model, MBD eliminates the need for paper-based drawings and multiple physical prototypes. This cuts down on scrap, rework, and unnecessary iterations, saving both time and materials.
Precise tolerancing and specifications help optimize material usage from the start, minimizing production errors and rejected parts. With all data stored digitally, teams can more easily assess environmental impact, plan for end-of-life strategies, and make informed decisions about materials.
MBD not only improves product quality – it also supports a more efficient, environmentally responsible development process from concept to production.
Bring your product development into the modern era with Autodesk’s MBD software. Inventor, our 3D CAD software, supports an MBD approach with features that elevate your design process.
Create semantic PMI directly on 3D models, generate automated 2D views from annotated 3D data, and export comprehensive 3D PDFs. An intuitive interface lets you easily manage GD&T, surface finishes, and other vital product information.
Whether you’re in aerospace, automotive, or consumer products, Inventor encourages you to create, validate, and communicate your designs with unmatched efficiency.
Industry leaders are using Autodesk’s MBD software to shake up their processes and stay ahead of the competition.
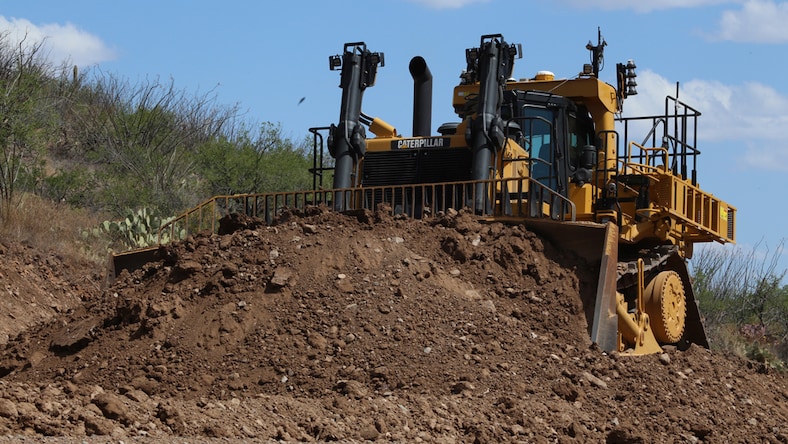
CATERPILLAR
Heavy equipment leader Caterpillar uses MBD for its initiatives, such as these semi-autonomous construction vehicles.
Image courtesy of Caterpillar
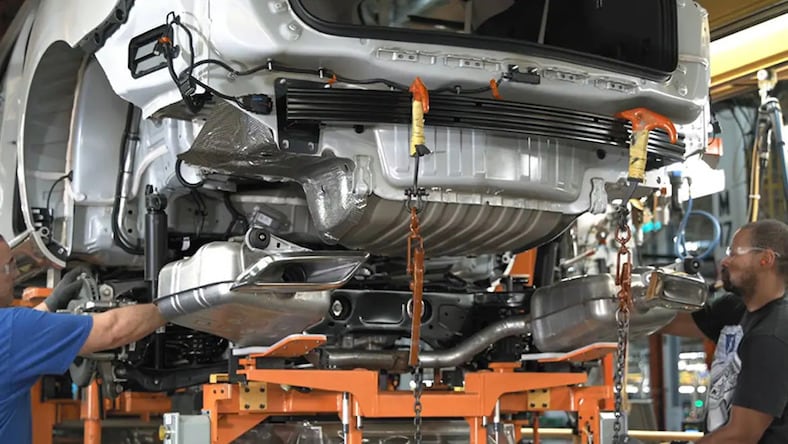
GENERAL MOTORS
Generative design early adopter General Motors has also adopted MBD for its design and manufacturing processes.
Image courtesy of General Motors
XOMETRY
This on-demand manufacturer highlights the time-saving benefits of using model-based definition and other product manufacturing information (PMI).
Image courtesy of Xometry
Don’t tolerate assembly problems; this Autodesk University class shows how the Tolerance Analysis plug-in for Inventor helps you manufacture right the first time.
Learn how defining a CAD model with MBD saves time and adds value to downstream supply chain processes at Autodesk University.
See how CAD data is consumed by production engineering and CAM systems and why center-tolerance models are a best practice for providing CAD data for manufacturing.
With the basics mastered, discover how to create an advanced MBD in Inventor with these useful tips and tricks from the Autodesk support team.
Learn what MBD means from an industry perspective and how model-based practices are being adopted.
Get a deep dive into using Inventor to become a success, whatever your profession or product. Explore how the process drives values to the supply chain.
MBD is an acronym for model-based definition, which annotates a 3D model with all the vital non-geometric information needed for manufacturing and inspection, such as dimensions, tolerances, symbols, finishes, and materials. MBD is a deliverable that comes embedded within a 3D model.
Autodesk Inventor software also uses the acronym 3DA (three-dimensional annotation) synonymously with MBD.
MBD and MBE are two sides of the same model-based coin, where the 3D model is the centerpiece around which design, engineering, manufacturing, and inspection processes are built.
Model-based definition (MBD) annotates a 3D model with the non-geometric information needed for manufacturing and inspection.
On the other hand, the term model-based enterprise (MBE) denotes a product development organization that has extrapolated the model-based ethos as far as possible. An MBE may use a 3D model as a single source of truth to inform decision-making and provide insights for design, engineering, internal and external supply chain processes, customer support, and more.
Product manufacturing information (PMI) includes several types of data describing a designed part or assembly, such as dimensions, tolerances, materials, and surface finishes. Model-based definition (MBD) is the technology for embedding PMI as metadata into a 3D model to eliminate the older method of conveying PMI through 2D drawings.
By including accurate PMI in a CAD model’s MBD annotations, that data is readily available as a single source of truth at every step of the product’s lifecycle.
Digital product definition (DPD) is the broader concept of using digital data to define a product, which can include 2D and 3D representations. Model-based definition (MBD) is a specific subset of DPD that focuses on using 3D CAD models as the main source of product definition, so you don’t need separate 2D drawings.
MBD improves quality control by reducing errors in communication and manufacturing prep time, maintaining the accurate and consistent transfer of data.
Yes, MBD integrates with various digital tools like product lifecycle management (PLM) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) systems, for improved efficiency.
Yes, by keeping all product information in the 3D model, MBD improves communication and collaboration between departments and global teams.
MBD is particularly beneficial for industries that require tight tolerances and precise data management, such as aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing.
Yes, MBD reduces costs by eliminating the need for producing, storing, and managing 2D drawings, thus reducing waste from scraps and rework.